DeepSeek (深度求索) is a Chinese artificial intelligence company based in Hangzhou and founded in 2023 by Liang Wenfeng.
Liang, a co-founder of the hedge fund High-Flyer, spun off DeepSeek to pursue artificial general intelligence (AGI) research with a focus on cost-effective, open-source large language models.
In late 2024 and 2025, DeepSeek stunned the AI community by releasing models that rival the performance of Western counterparts like OpenAI’s GPT-4 at a fraction of the training cost.
This commitment to innovation and transparency has quickly elevated DeepSeek into a major AI player on the global stage.
DeepSeek V2 – Efficient Giant (236B Parameters)
DeepSeek-V2, launched in late 2024, marked a major milestone for the company. It is a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) language model with 236 billion total parameters (about 21 billion active per token) and a context window up to 128K tokens. MoE design allows the model to activate only relevant “experts” for each query, greatly improving efficiency.
In fact, DeepSeek-V2 achieved stronger performance than the company’s earlier 67B dense model while cutting training costs by ~42% and reducing memory usage (KV cache) by over 90%. It was pretrained on an enormous corpus of 8.1 trillion tokens and then fine-tuned with supervised instruction and reinforcement learning, yielding remarkable results on benchmarks.
For example, V2 demonstrated high proficiency on Chinese knowledge tests (scoring 81.7 on C-Eval, far above previous models) and solid coding ability. Crucially, DeepSeek released V2’s weights openly, allowing researchers and developers worldwide to download and run it.
This made V2 one of the most powerful open-source LLMs of its time, balancing strength and efficiency in a way that was highly accessible.
DeepSeek V3 – Scaling Up to 671B and Closing the Gap
Introduced in December 2024, DeepSeek-V3 took the model size and performance to a new level. V3 is an MoE model with a staggering 671 billion parameters (with ~37B active per token).
Despite its massive scale, V3 was trained with remarkable efficiency – roughly 2.8 million GPU hours on Nvidia H800 chips (around $5.6 million cost), which is only a small fraction of the tens of millions reportedly spent to train GPT-4.
This efficiency is largely thanks to the MoE architecture: the model doesn’t use all 671B parameters at once, but routes queries to the most relevant experts. DeepSeek-V3 was released in two versions: a Base model and a Chat model.
The Base model is the raw LLM pre-trained on vast text data, while the Chat model underwent additional instruction tuning and reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) to make it more conversational and helpful. The DeepSeek-V3 Chat model quickly proved adept at complex tasks like coding and math problem-solving, even comparing favorably to top-tier systems like GPT-4 and Meta’s large Llama models in evaluations.
Notably, V3 supports an extra-long 128K token context, enabling it to handle extremely lengthy inputs or documents. Both the base and chat V3 models were released under open licenses (MIT-based), meaning anyone can use or deploy them commercially.
In early 2025, the DeepSeek team further refined V3’s techniques – a March 2025 update (sometimes called DeepSeek-V3-0324) applied lessons from the reasoning model to improve V3’s coding and reasoning skills, reportedly allowing it to outperform an early GPT-4.5 on math and coding benchmarks.
In short, V3 established DeepSeek as a bona fide peer to the best AI models in the world.
DeepSeek R1 – Transparent Reasoning with “Thinking” Mode
Just weeks after V3, DeepSeek unveiled DeepSeek-R1 (released in January 2025) as a specialized reasoning model built on the V3 base. R1’s development was unique: an experimental precursor model (R1-Zero) was trained purely via reinforcement learning without supervised fine-tuning, giving it strong reasoning emergent abilities but with some quirks (like occasional repetitive rambling or mixing languages).
The final R1 model then introduced a more refined multi-stage training pipeline – essentially adding a brief supervised tuning step (“cold-start” data) to ground the model before applying RL, which greatly improved its accuracy, coherence, and readability. The defining feature of DeepSeek-R1 is its “think-before-answering” approach.
R1 internally generates a step-by-step chain-of-thought (enclosed in special <think> tags) prior to giving a final answer. In practical terms, this means R1 not only gives answers but also explains how it derived them – a level of transparency rarely seen in other chatbots.
This makes R1 especially powerful for tasks requiring logical reasoning and multi-step problem solving. It excels at complex mathematics, coding challenges, scientific reasoning, and even planning tasks for AI agents.
On quantitative benchmarks, R1 rivals or even surpasses OpenAI’s own cutting-edge “o1” reasoning model in domains like math, coding, and logical reasoning.
In fact, DeepSeek noted that R1 is 20–50× cheaper to run than the comparable OpenAI model for the same tasks, highlighting a huge efficiency win. Like V3, R1 is fully open-source (MIT license) and stands as the most powerful open reasoning LLM available as of 2025. It powers DeepSeek’s official chatbot service and has been adapted by many developers for their own applications.
A subsequent update in May 2025 (DeepSeek-R1-0528) further boosted R1’s reasoning depth and cut down its hallucination rate by nearly half, bringing its performance closer to the absolute state-of-the-art models like OpenAI’s next-gen systems and Google’s Gemini.
In essence, R1 demonstrated that AI can not only give answers but show its work – a game-changer for trust and verifiability in AI responses.
Open-Source and Privacy Considerations
A core philosophy of DeepSeek is its commitment to open-source development and community access. All major DeepSeek models (V2, V3, R1, etc.) have been released as open weights, accompanied by permissive licenses that allow commercial use and self-hosting.
This open approach contrasts with closed-source models like GPT-4 or Anthropic’s Claude, and it carries important privacy advantages.
Because anyone can download and run DeepSeek models on their own hardware or private cloud, users are not forced to send sensitive data to a third-party API or server when using the model.
For example, companies can deploy DeepSeek behind their firewall, or individuals can run it on local machines, ensuring that no personal data leaves their environment.
Even for public use cases, the model’s transparent reasoning tokens (the <think> chains in R1) provide interpretability – you can see why the AI arrived at an answer, which increases trust. It’s worth noting the context of server location as well: DeepSeek’s official services are hosted in China (and the model was developed with Chinese funding), which means data sent to the official API or app could reside on Chinese servers. Some users may hesitate to route data through servers in certain jurisdictions.
However, since DeepSeek’s models are open-source, the community has stepped up to host them on servers around the globe. Essentially, you choose where and how the model runs – a boon for privacy-conscious users.
As one AI commentator put it, whenever you use an online LLM, “the real question is: Which government are you comfortable handing your data to?”. DeepSeek’s openness gives you the option to avoid handing data to any foreign entity by running the AI yourself.
In summary, DeepSeek has uniquely combined cutting-edge performance with an open model release, empowering users with both control and transparency.
DeepSeek in the Global LLM Landscape
DeepSeek’s rapid progress has made it a prominent name in the global large-language-model (LLM) landscape, right alongside the likes of OpenAI’s GPT-4, Google’s PaLM/Gemini, and Anthropic’s Claude.
When OpenAI’s ChatGPT (GPT-4) took the world by storm in 2022–2023, many Chinese efforts struggled to catch up. DeepSeek has now flipped that narrative.
Its flagship models (V3 and R1) are on par with the most advanced models from OpenAI and Meta according to many experts. In Silicon Valley circles, engineers have praised DeepSeek-V3 and R1 for matching GPT-4’s capabilities in key areas, from writing code to answering complex questions. Impressively, DeepSeek was the first to open-source a model that can actually outperform GPT-4 on certain benchmarks.
For instance, the updated V3 (v3-0324) has been reported to slightly outscore GPT-4.5 in mathematics and coding tasks. Likewise, R1’s specialized reasoning often beats out other reasoning-focused AI models.
Some comparisons show that DeepSeek-R1 outperforms Anthropic’s Claude (v3.5) on coding and math-intensive benchmarks, areas where chain-of-thought logic is crucial.
This is a remarkable feat for an open model coming from a young startup. DeepSeek’s emergence is also reshaping AI geopolitics – it demonstrated that a relatively small team (albeit well-funded via High-Flyer) in China could produce a GPT-4-level model cheaply and quickly, raising questions about the massive spending by U.S. tech giants.
Of course, there has been skepticism too: observers have questioned whether DeepSeek somehow accessed more compute power than acknowledged.
But conspiracy theories aside, the consensus is that DeepSeek has achieved something extraordinary. In the global AI race, it stands out as the leading open-source contender, providing a viable alternative to the closed models from OpenAI, Google, and others.
As of 2025, any discussion of state-of-the-art AI models now includes DeepSeek alongside GPT-4, Claude, and the rest – a testament to how quickly DeepSeek has joined the top tier.
Use Cases and Adoption
DeepSeek’s models have found a wide range of applications thanks to their strong performance and open availability.
On the software development front, coding assistance is a popular use case. The company released specialized coder models (e.g. DeepSeek-Coder V2) tuned for programming help, supporting hundreds of programming languages and offering up to 128K context for reviewing large codebases.
Developers use DeepSeek to generate code snippets, debug errors, and even design entire algorithms from scratch.
For more general problem-solving and STEM education, DeepSeek-R1 is a game-changer – it can walk through complex math problems step-by-step and tackle logical puzzles or scientific questions by explaining each step of the reasoning.
This makes it a powerful tutor-like tool for students and researchers who not only want answers but also clear explanations.
In fact, R1 has been used in solving advanced math competition problems and providing detailed proofs or rationales, something few other AI chatbots can do reliably.
Meanwhile, content creation and everyday assistance are squarely in DeepSeek-V3’s wheelhouse. Users employ V3 for writing help (drafting articles, summarizing text, creative storytelling), language translation, and general Q&A across both English and Chinese.
Its responses are fluent and informative, comparable to other top chatbots in quality.
Thanks to the free and open nature of DeepSeek’s chat models, adoption has been swift. By early 2025, the official DeepSeek AI Assistant app had soared in popularity – it even became the #1 free app on Apple’s App Store in the U.S., briefly unseating OpenAI’s own ChatGPT mobile app.
This surge was driven by users eager to try a ChatGPT-like AI without paywalls, as DeepSeek offered free access to its powerful model. Beyond the official app, the open-source community has embraced DeepSeek.
On platforms like Hugging Face, DeepSeek model checkpoints have been downloaded by researchers hundreds of thousands of times, and distilled smaller versions (e.g. a 33B parameter distilled model) have garnered over 1.8 million downloads for lighter-weight usage. Enthusiasts have integrated DeepSeek into all sorts of tools – from coding plugins in IDEs to AI assistants on forums.
Early adopters in education are also experimenting with DeepSeek as a virtual teaching assistant, leveraging its ability to show its work (which is great for helping students understand solutions).
The breadth of use cases continues to grow as more people discover that an open model can often meet their needs just as well as proprietary bots.
Whether it’s writing an essay, solving a tricky calculus equation, or generating a snippet of Python code, DeepSeek has found its way into daily workflows for many – all within just a year of its debut.
How to Access DeepSeek (Official and Unofficial)
Officially, users can access DeepSeek via the company’s own platforms. DeepSeek operates a web-based chatbot interface (the official DeepSeek Chat at chat.deepseek.com) and mobile apps for iOS/Android where anyone can converse with the AI.
Notably, the chat service has a Deep Thinking Mode toggle that lets users explicitly invoke R1-style chain-of-thought reasoning for more complex queries.
The official assistant is currently free to use, which has contributed greatly to its popularity.
For developers, DeepSeek provides a cloud API and SDK as well – the company offers endpoints for the DeepSeek-Chat model and the DeepSeek-Reasoner (R1) model, with pricing that undercuts many competitors.
This means companies can integrate DeepSeek’s capabilities into their own products or services by calling an API, much as they would with OpenAI’s or Anthropic’s offerings.
Beyond the official channels, one of the advantages of an open model is the plethora of community-run access points.
The AI community has deployed DeepSeek models on various platforms for easier public access.
For example, the Together AI platform hosts DeepSeek models and even provides OpenAI-compatible APIs so you can “switch out” GPT-4 for DeepSeek with minimal code changes.
Researchers have also set up public inference endpoints on cloud services and Hugging Face Spaces where anyone can try a quick demo of DeepSeek without installation.
There are fan-hosted websites like Deep AI Chat that offer a simple chat interface to DeepSeek’s models outside of the official site – these are great for users who might not have a Chinese phone number or other requirements for the official app.
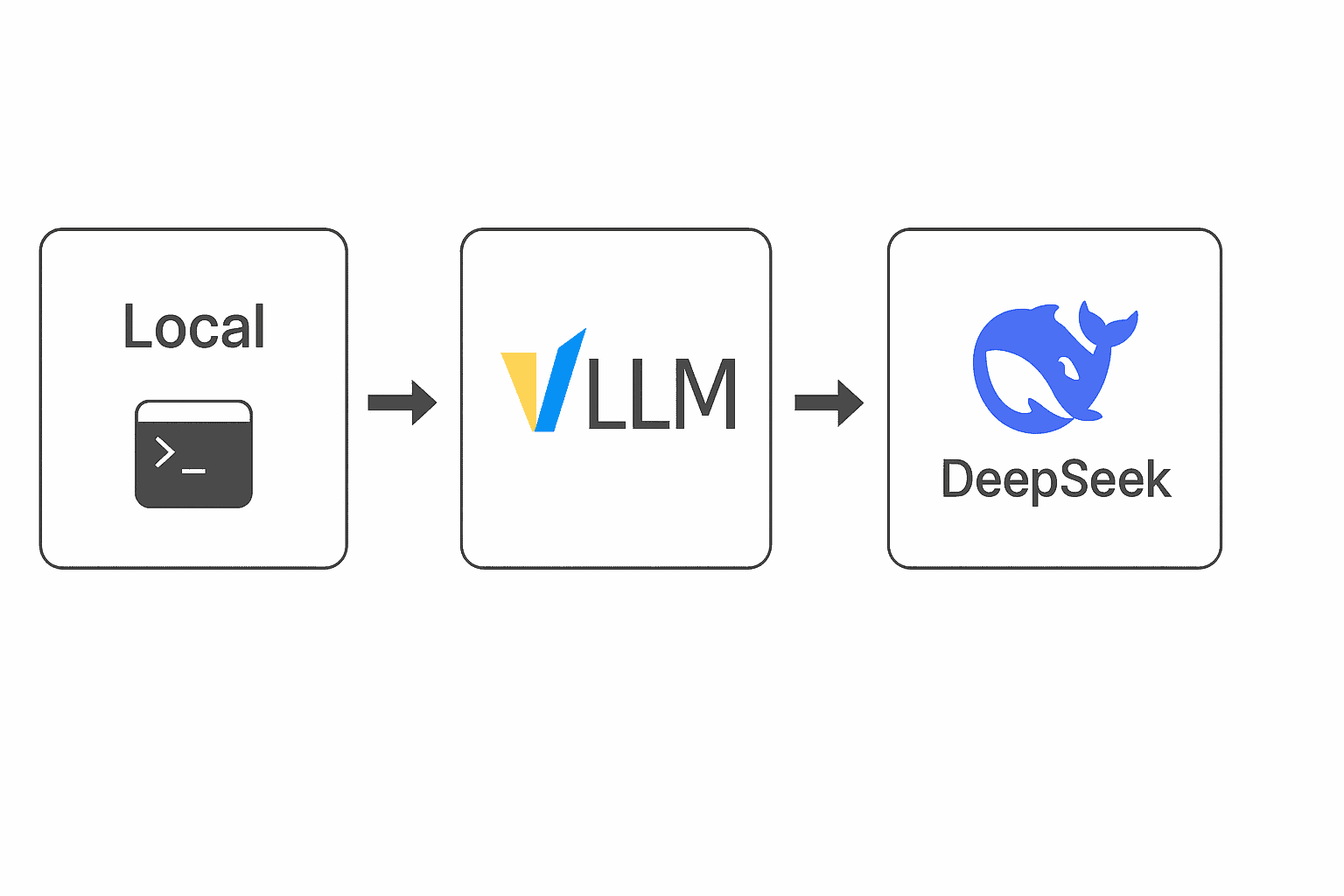
Essentially, if you want to experiment with DeepSeek, you have many options: download the weights and run it locally, use a hosted API (official or third-party), or hop onto a community web UI.
This wide availability, from official to unofficial avenues, underscores DeepSeek’s mission of widespread access. Whether you’re an AI engineer deploying a private model instance or an everyday user looking for a free AI chatbot, DeepSeek is within reach.
And with its open-source DNA, the number of access points and integrations is only expected to grow, solidifying DeepSeek’s presence in the AI chatbot ecosystem.